- (A) The flow speed must be greater in the upper section.
- (B) The upper section must have a larger diameter than the lower section.
- (C) The upper section must have a smaller diameter than the lower section.
- (D) No statement can be made without knowing the value of h.
- (E) No statement can be made without knowing the volume flow rate.
where y and x are in metres and t is in seconds. The frequency of this wave is:
- (A) 0.500 Hz
- (B) 2.00 Hz
- (C) 1.00 Hz
- (D) 3.14 Hz
- (E) 2.50 Hz
- (A) 40 dB
- (B) 20 dB
- (C) 0 dB
- (D) 60 dB
- (E) none of the options given
- (A) fR < f & fB < f
- (B) fR < f & fB > f
- (C) fR > f & fB < f
- (D) fR > f & fB > f
- (E) fR = f = fB
- (A) 0
- (B) ½ A
- (C) A
- (D) 2 A
- (E) 4 A
- (A) ¼ f
- (B) ½ f
- (C) f
- (D) 2 f
- (E) 4 f
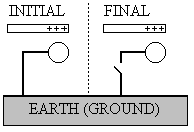 |
|
- (A) F/16
- (B) F/4
- (C) F
- (D) 4 F
- (E) 16 F

The electric field at P due to Q1 has a magnitude |E1| and the electric field at P due to Q2 has a magnitude |E2|. |E2| > |E1|. The total (net) electric field at P is:
- (A) directed to the right with magnitude |E2| + |E1|.
- (B) directed to the right with magnitude |E2| - |E1|.
- (C) directed to the left with magnitude |E2| + |E1|.
- (D) directed to the left with magnitude |E2| - |E1|.
- (E) 0
- (A) 0
- (B) 1.5 V
- (C) 3 V
- (D) 6 V
- (E) 18 V