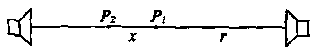Questions from April 1997 Physics 111.6 Final Examination
Al. A rock is thrown vertically upwards from the surface of the earth. The rock rises to some maximum height and then falls back towards the ground. Which of the following statements is correct if air resistance is neglected?
(A) As the ball rises, its acceleration vector points upward.
(B) The velocity of the ball changes at a constant rate throughout the flight.
(C) The acceleration of the ball is zero when the ball is at its highest point.
(D) The speed of the ball is negative while the ball is falling back towards the ground.
(E) The velocity and acceleration of the ball always point in the same direction.
A2. An object moves in the eastward direction at constant speed. A net force directed northward acts on the object for 5 s. At the end of the 5-second period, the net force drops to zero. Which of the following statements is necessarily true?
(A) The object will be moving eastward when the force drops to zero.
(B) The final velocity of the object will be directed north of east.
(C) The acceleration of the object while the force is acting will he directed north of east.
(D) The direction of the object's acceleration while the force is acting depends on how fast the object was initially moving.
(E) The magnitude of the object's acceleration while the force is acting depends on how fast the object was initially moving.
A3. An object has a weight W while on the surface of the Earth. What is the weight of the object on another planet which has twice the radius and twice the mass of the Earth?
(A) ¼ W (B) ½ W (C) W (D) 2 W (E) 4 W
A4. Two stones are thrown from the top of a tall building. Stone A is thrown straight upward with a speed of 20.0 m/s. Stone B is thrown straight downward, also with a speed of 20.0 m/s. Air resistance is negligible. Which statement best describes the speed of each stone just prior to its impact with the ground?
(A) Stone A will have a higher speed than stone B.
(B) Stone B will have a higher speed than stone A.
(C) Both stones will have the same speed.
(D) It is impossible to know the relationship between the two speeds without knowing the height of the building.
(E) None of the above statements is correct.
A5. Momentum will be conserved in a two-body collision only if
(A) both bodies come to rest.
(B) the collision is perfectly elastic.
(C) the kinetic energy of the system is conserved.
(D) the net external force acting on the two-body system is zero.
(E) the internal forces of the two-body system cancel in action-reaction pairs.
A6. A solid disc rotates about a fixed axis through its centre with a constant, positive angular acceleration. Which of the following statements is true concerning the tangential acceleration of a point on the rim of the disc?
(A) It is zero.
(B) It is constant in both magnitude and direction.
(C) The magnitude is constant, but the direction is continually changing so that it always points towards the rotation axis.
(D) The magnitude is constant, but the direction is continually changing so that it always points in the direction of motion of the point on the rim.
(E) The direction is constant, but the magnitude is continually changing.
A7. Which of the following statements best describes the principle of operation of a hydraulic jack?
(A) A small change of pressure in the small cylinder results in a large change of pressure in the large cylinder.
(B) A large change of pressure in the small cylinder results in a small change of pressure in the large cylinder.
(C) The same change of pressure occurs throughout the system, resulting in a large force on the large piston.
(D) A small amount of work done on the small piston results in a large amount of work done on the large piston.
(E) The force exerted on the small piston equals the force acting on the large piston.
A8. Two sounds differ in intensity by a factor of two. The difference in their intensity levels is:
(A) less than 10 dB (B) 20 dB (C) 40 dB (D) 100 dB (E) 200 dB
A9. Two speakers, facing each other and separated by a distance 2r, are emitting identical, in-phase sound waves of wavelength l. A microphone initially at point P1, equidistant from each speaker, is slowly moved toward one of the speakers until the detected sound intensity reaches a minimum (destructive interference) at point P2. The distance x between locations P1 and P2 is:
|
|
(A) l (B) l/2 (C) l/4 (D) 3l/2 (E) 2l
A10.Two conducting spheres of equal size are separated by a distance r. Initially, one of the spheres is uncharged and the other has a charge of –6 Q. Without changing their separation, the spheres are connected by a conducting wire. The electrostatic force between the spheres is now:
(A) 0 (B) kQ2/r2 (C) 6kQ2/r2 (D) 3kQ2/r2 (E)9kQ2/r2
A11.Consider a point P midway between two positive charges of equal magnitude +Q that are separated by a distance 2d. Which of the following statements is correct concerning the net electric field Enet and net absolute electric potential Vnet at P due to the two charges?
|
(A) Enet = 2(kQ/d2) to the right and Vnet = 0 (B) Enet = 2(kQ/d2) to the left and Vnet = 0 (C) Enet = 2(kQ/d2) to the right and Vnet = 2kQ/d (D) Enet = 0 and Vnet = 0 (E) Enet = 0 and Vnet = 2kQ/d
|
|
A12.Two wires A and B are made of the same material and have the same diameter. Wire A is twice as long as wire B. If each wire has the same potential difference across its ends, which of the following statements is true concerning the current in wire A?
(A) It is one-fourth that in B.
(B) It is four times that in B.
(C) It is equal to the current in B.
(D) It is half as much as that in B.
(E) It is twice as much as that in B.
A13.A proton travelling due north enters a region that contains both a magnetic field and an electric field. The electric field lines point due west. It is observed that the proton continues to travel in a straight line due north. In which direction must the magnetic field lines point?
(A) up (B) down (C) east (D) west (E) south
A14.When an object is placed 20 cm in front of a diverging lens, a reduced image is formed. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) The image is inverted.
(B) The image could be real.
(C) The image distance must be greater than 20 cm.
(D) The focal length of the lens could be less than, equal to, or greater than 20 cm.
(E) The refractive power of the lens must be greater than 0.05 diopters.
A15.The middle of the first-order maximum, adjacent to the central bright fringe in Young's double slit experiment, corresponds to a point where the optical path length difference from the two slits is equal to:
(A) l (B) 0 (C) l/2 (D) l/4 (E) none of the above
A16.Which one of the following problems did Max Planck solve using an explanation which eventually led to the development of the "quantum" hypothesis?
(A) the photoelectric effect
(B) the uncertainty principle
(C) blackbody radiation curves
(D) the generation of X-rays
(E) natural radioactivity
A17.In the Compton effect, a photon of wavelength land frequency f hits an electron which is initially at rest. Which occurs as a result of the collision?
(A) The photon is completely absorbed.
(B) The photon loses energy, so the final photon has a frequency less than f.
(C) The photon loses energy, so the final photon has a wavelength less than l.
(D) The photon gains energy, so the final photon has a frequency less than f.
(E) The photon gains energy, so the final photon has a wavelength less than l.
A18.In what types of radioactive decay are the nucleon numbers of the parent and daughter nuclei different?
(A) alpha decay
(B) beta decay
(C) gamma decay
(D) both alpha decay and beta decay
(E) both beta decay and gamma decay
A19.Which one of the following statements is true concerning the radioisotope 146C that is used in carbon dating?
(A) It is produced by living cells.
(B) It is produced during b– decay.
(C) It is produced by the decay of 126C.
(D) It is produced by cells after they have died.
(E) it is produced by cosmic rays striking the atmosphere.
A20.Complete the following nuclear reaction: 42He + 126C ® n + p + ?
(A) 168O (B) 158O (C) 147N (D) 149F (E) 157N
B1. A bullet is fired vertically upwards from the ground with a speed of 300 m/s. Find the time that the bullet is in the air.
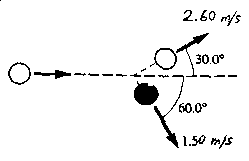
B2. Billiard balls have a mass of 0.170 kg. The diagram shows a billiard ball (black) being struck by a cue ball (white). What is the speed of the cue ball before the collision?
|
|
B3. A spherical star of mass 2.00 ´ 1031 kg and radius 7.50 ´ 108 m is rotating with an angular velocity of 0.105 rad/s. Internal forces cause the star to collapse to a new radius of 1.25 ´ 108 m. Assuming the star to be a uniform sphere before and after the collapse, calculate the angular velocity of the collapsed star.
B4. For testing its suitability for space flight, a computer is bolted to a spring-mounted platform as shown. The platform is made to oscillate in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 2.50 cm. Calculate the oscillation frequency f that gives a maximum acceleration of 15.0 ´ g.
|
|
B5. A string of mass 1.20 g and length 8.50m is under a tension of 1.60 N. The string is oscillating in a standing wave pattern with nodes at each end and two nodes between its ends. Calculate the frequency of vibration of the string.
B6. A very small speaker, with a power output of 100 W, emits sound uniformly in all directions. What is the sound intensity at a distance of 10.0 m from the speaker?
B7. A diamond ring is placed 30.0 cm in front of a lens. The image of the ring is inverted and 0.400 times the size of the ring. Find the focal length of the lens.
B8. When light from a mercury source passes through a diffraction grating, the third-order maximum of the 578-nm yellow line occurs at the same location as the fourth-order maximum of a different wavelength Calculate the wavelength of the fourth-order line.
B9. The work function for a particular metal is 4.20 eV. What is the minimum frequency of photons needed to eject electrons from the metal surface with a maximum kinetic energy of 1.00 eV?
B10. Calculate the binding energy (in MeV) of 1123Na (atomic mass = 22.989767 u).
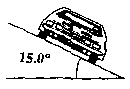
C1. A car of mass 1500 kg is travelling around a banked curve which is inclined at an angle of 15.0° above the horizontal.
|
|
(a) The car's path is circular with a radius of curvature of 100 m. Assuming that the road surface is frictionless, calculate the speed of the car such that it remains on the banked curve.
(b) Real road surfaces are not frictionless. Suppose the driver stops the car on the banked curve. Calculate the magnitude of the total static friction force between the car's tires and the road surface.
(c) It starts to rain and the car slides sideways down the inclined road surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the road is 0.115, determine the acceleration of the car as it slides.
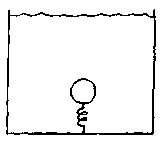
C2. A ball of mass 0.450 kg is anchored to the bottom of a swimming pool by an ideal spring of force constant 60.0 N/rn attached to the pool's bottom. The spring stretches 4.20 cm from its unstretched length as the ball reaches equilibrium at a depth of 3.50 m. The density of water is 1000 kg/m3.
|
|
(a) Calculate the magnitude of the force exerted on the ball by the spring.
(b) Calculate the radius of the ball.
(c) Assuming the atmospheric pressure is 1.02 ´ 105 Pa, calculate the absolute pressure at the depth of the ball.
C3. The energy released when a radioisotope decays maybe used to produce electricity to power such things as interplanetary probes. Consider the radioactive nucleus 21084Po (polonium) which decays by alpha emission to 20682Pb (lead) with a half-life of 138.4 days
Atomic mass of 21084Po = 209.982848 u
20682Pb = 205.974440 u
42He = 4.002603 u
(a) Calculate the energy released (in MeV) in the decay of each 21084Po atom.
(b) If a 1.00-g sample of 21084Po initially contains 2.87 ´ 1021 atoms. what is the initial decay rate from this sample (in Bq)?
(c) How many of this initial number of atoms remain after one year?
(d) What is the average power output (in W) from the decay of 21084Po in this sample during the first year?